I am building an SFFPC

A Small Form Factor PC, or SFFPC, is a compact computer system designed with a significantly smaller volume than a standard ATX tower. To give you a perspective, SFFPCs are often compared to shoeboxes, with a volume of approximately 10 liters. There is an even smaller category known as Ultra Small Form Factor, represented by devices like NUCs and HP Elite, which utilize low-power components commonly found in laptops. However, our focus here lies on the category just above this, as we aim to maximize the use of standard desktop components within a minimized enclosure.
At first glance, you might think this is a straightforward endeavor, but in reality, it comes with numerous challenges. The limited volume of the enclosure introduces significant constraints, affecting the temperatures during operation. Therefore, it becomes crucial to select an appropriate cooling solution tailored to both your CPU and GPU, as well as the form factor of your case. Not everything will fit, and this also applies to other components like the graphics card, whose dimensions increase with each generation, thus requiring a delicate balancing act.

Another crucial consideration is noise. While it might not be a top priority for gamers who play with headphones on, individuals utilizing the computer for resource-intensive tasks such as 3D rendering or video editing prefer a silent PC. However, cooling solutions can often be noisy, leading to yet another decision to be made.
It's worth reiterating that temperature is the arch-nemesis of performance in a PC, and the goal here is to achieve maximum performance. As you gain a better understanding of the challenges of this PC form factor, you'll need to skillfully select your components to strike the right balance among volume, temperature, performance, and noise.

Additionally, there's the cost factor to consider, as building an SFFPC typically comes at a higher price.
At this juncture, you should be in a position to choose your path:
- If you lean towards getting the most performance at the lowest cost and aren't bothered by the size of the PC, then sticking with ATX is the way to go.
- However, if you have a penchant for challenges and value the compact size of your PC, welcome to my first guide, which aims to assist you in choosing your components.
Processor
TDP
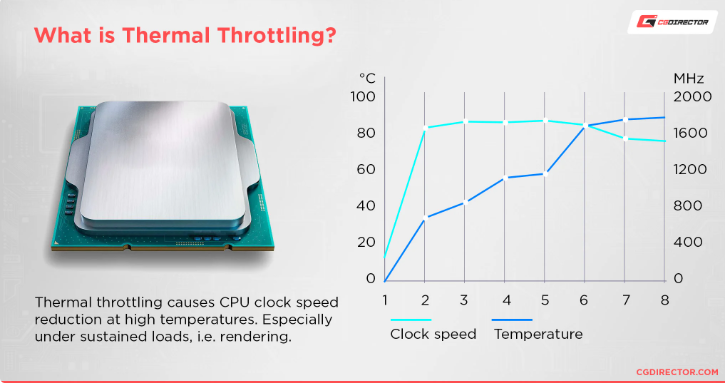
The Thermal Design Power (TDP), expressed in watts, serves as an indicator of a processor's heat output, distinct from its actual power consumption. This value plays a pivotal role in the selection of an appropriate cooling solution for your system. Going beyond a processor's designated TDP can result in thermal throttling, a process where the CPU's frequency is deliberately lowered to avert overheating. Operating electronic components at elevated temperatures not only compromises their performance but can also induce anomalies, failures, and even permanent damage. The TDP figure is influenced by a combination of factors, encompassing the process node, number of transistors, cores, voltage, cache size, and the presence and utilization of an integrated GPU. Careful consideration of these variables is essential to ensure your processor functions optimally while maintaining safe thermal conditions.
Manufacturer : Intel vs AMD
When it comes to CPU manufacturers, the two main players are AMD and Intel. Intel is often favored for its superior performance and overall value for money, making it an attractive choice for many users. However, it's essential to note that Intel processors typically exhibit higher power consumption, which can pose challenges for Small Form Factor PCs (SFFPCs) unless equipped with expensive cooling solutions. In the realm of SFFPCs, where power efficiency is of paramount importance, AMD emerges as a more favorable alternative. Notably, there are several intriguing SFFPC processors on the market, including the i5-13600K, Ryzen 7-7700X, and, particularly for gaming enthusiasts, the Ryzen 7-5800X3D, each offering a unique blend of performance and efficiency tailored to the demands of compact computing.

Cache
The CPU cache is a vital component that enhances program execution speed. Acting as a high-speed, short-access memory, the cache stores frequently accessed data, reducing the CPU's reliance on accessing data from the slower system RAM. What sets the cache apart is its remarkable speed; cache access times are notably faster than those of RAM, with various cache levels offering different access times. In resource-intensive tasks like gaming, the cache's size becomes of paramount importance. A larger cache serves to significantly reduce the CPU's need to access the system's RAM, resulting in smoother, more responsive performance, ultimately making it an indispensable asset for demanding computing endeavors.
Socket
The CPU socket serves as the physical interface connecting your CPU to the motherboard. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring compatibility between your selected processor and motherboard. Different CPUs are designed to fit specific socket types, so matching them correctly is crucial. For example, the Ryzen 7-7700X utilizes the AM5 socket, the Ryzen 5-5800X is compatible with the AM4 socket, and the i5-13600K pairs with the LGA1700 socket. This careful alignment of CPU and socket is essential.
RAM compatibility
Matching your RAM to your CPU is a critical consideration, as RAM size and frequency compatibility can vary. Adhering to the manufacturer's specified limits is essential to ensure optimal performance and system stability. For instance, the Ryzen 7-7700X supports a maximum of DDR5-5200 RAM and the Ryzen 5-5800X is compatible with up to DDR4-3200. Understanding and adhering to these limits ensures your CPU and RAM work seamlessly together to deliver the best possible performance for your specific computing needs.

Overclocking
While the prospect of overclocking, which entails boosting a CPU's clock frequency, might be enticing for some, it contradicts the fundamental principles of Small Form Factor PCs (SFFPCs). Overclocking typically demands a more robust cooling solution and a larger case to manage the increased heat generated. It's important to note that not all CPUs are designed for overclocking. In Intel's lineup, models intended for overclocking are labeled with a "K" suffix, signifying their unlocked potential. On the other hand, all AMD Ryzen CPUs support overclocking, providing users with the flexibility to enhance performance within the parameters of their SFFPC build, although it should be approached with caution, keeping thermals and case constraints in mind.
Motherboard
When it comes to selecting a motherboard for your SFFPC build, several key considerations can significantly impact your system's functionality. Once you've determined the appropriate CPU socket for your build, the next step is to find a motherboard in the ITX form factor. Here are some crucial aspects to bear in mind during the selection process.
RAM support
ITX motherboards have specific limitations, particularly concerning RAM compatibility. Ensure that your chosen motherboard supports the desired RAM type, whether it be DDR5 or DDR4. If your CPU supports DDR5, and your budget allows, opting for this newer standard is often advantageous.

BIOS Flashback
A valuable feature to look for in a motherboard is the capability to perform a BIOS flashback. This functionality allows you to update or reflash the BIOS without having installed RAM or a CPU. It's exceptionally convenient for testing new features or accommodating compatibility with new processors, simplifying the upgrade process.
Connectivity
Pay close attention to the available connectivity options, as ITX motherboards often have limited space for ports and slots. Your preferences matter here. Whether you prioritize multiple USB-A ports over USB-C or require a 7.1 audio setup, thoroughly examine the motherboard's specifications to ensure it aligns with your connectivity needs.

M.2 PCIe slots
ITX motherboards typically feature at least one M.2 PCIe slot for the insertion of M.2 SSDs. These drives are not only compact but also offer high performance. With two M.2 slots, you can dedicate one for booting and the other for data storage, optimizing your storage configuration.

PCIe slots
Most ITX motherboards come equipped with a single PCIe slot, which is typically used for the graphics card. However, verify the available PCIe version. The communication speed is notably enhanced with PCIe 4 compared to PCIe 3, provided that both your graphics card and CPU support this standard. It's worth noting that some motherboards may support both versions and can be configured in the BIOS accordingly.
Wifi 6
With Wi-Fi 6 becoming a standard feature, it's almost expected on modern motherboards. Ensure that your chosen ITX motherboard includes Wi-Fi 6 support, as it offers improved wireless connectivity and performance, ensuring a more seamless online experience for your SFFPC.
Graphic card
Are you a gamer? If not, there's no need to chase after large, expensive, power-hungry graphics cards. Instead, consider a CPU with integrated graphics (often referred to as an APU in the case of AMD) or an entry-level graphics card.
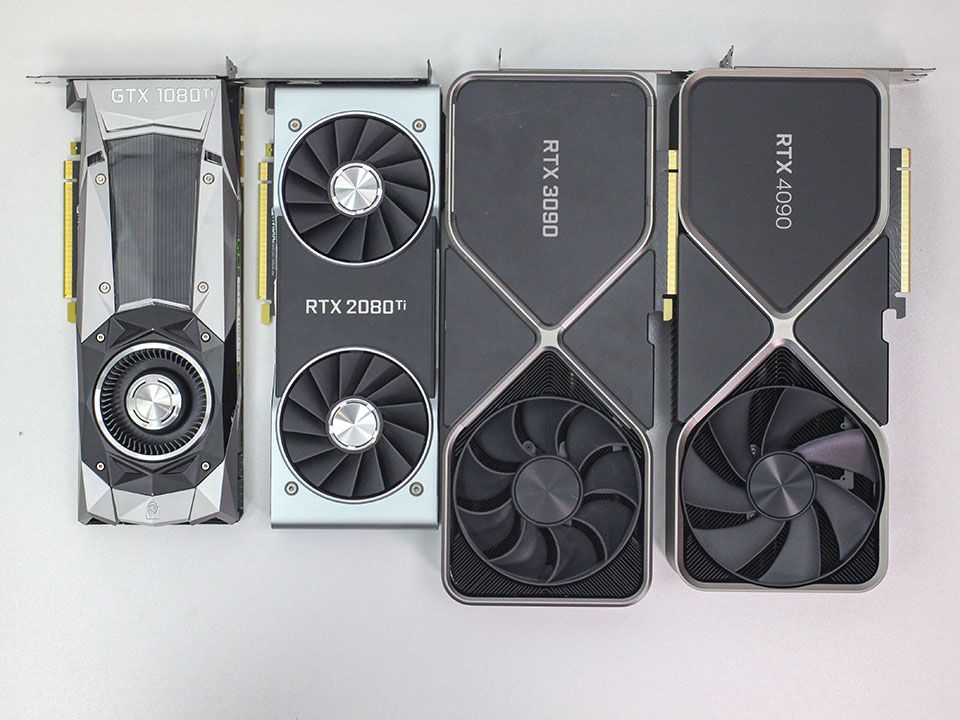

For gamers, the current landscape offers a challenging scenario. Graphics cards have soared to exorbitant prices, making it necessary to allocate at least $800 for something decent and potentially up to $1200 for a high-end card.
The issue doesn't end there. Graphics card sizes and power consumption are on the rise, requiring careful consideration when selecting your case. If you opt for a minimalist design to maximize space-saving, cooling becomes a significant challenge. Adequate space is necessary for proper airflow or for accommodating cooling solutions, such as liquid cooling.
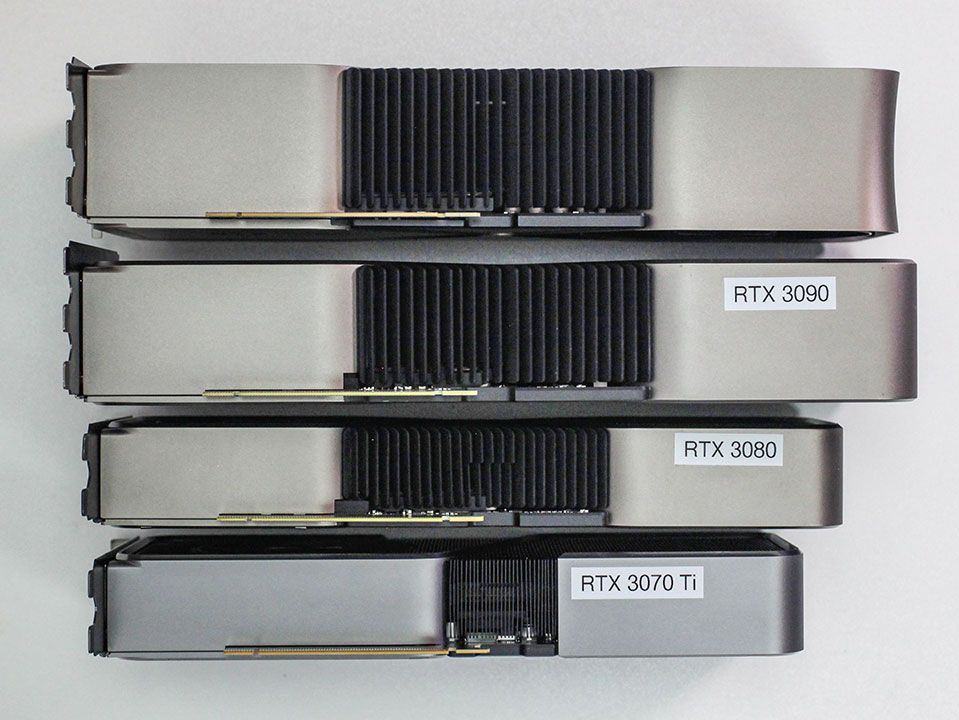

Another critical factor to keep in mind with high-end graphics cards is their capacity to run games in 4K at high frame rates. Before diving into the world of 4K gaming, ask yourself the following questions:
- Do you have a monitor capable of handling this resolution and high frame rates?
- Does your motherboard offer the necessary connectivity to utilize these capabilities? A DisplayPort 1.4 port, for instance, allows you to achieve 4K at 120 or 144Hz, while an HDMI port typically limits you to 60Hz.
Ultimately, the choice is yours and should align with your personal preferences and budget. It's essential to be honest with yourself about what you truly need from your SFFPC. The allure of an SFFPC lies in the balance between case size and machine power. If you're seeking excessive power, it might be more practical to opt for an ATX build, which would save you a lot of potential headaches in your pursuit of high-end performance.
RAM
Selecting the appropriate RAM for your Small Form Factor PC (SFFPC) is a crucial step in tailoring your system's performance to your needs. Here are some key considerations to guide your RAM selection.

Number of RAM Slots
The number of available RAM slots on your motherboard, as well as their individual capacities, plays a vital role in determining the optimal RAM configuration for your SFFPC. This directly affects your system's total memory capacity.
16GB as a Starting Point
As a starting point, 16GB of RAM is a solid choice for most SFFPC builds. It strikes a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness. However, it's essential to consider the maximum RAM frequency supported by your motherboard. If the motherboard specifies frequencies with an "(o.c)" notation, it means that the default RAM frequency may be lower than the memory module's maximum capabilities. In such cases, you may need to overclock your RAM from the BIOS to unlock its full potential. We'll explore the overclocking process in more detail shortly.
RGB or Non-RGB
The inclusion of RGB (colorful LED lighting) on your RAM modules is a matter of personal customization. If you enjoy the aesthetic appeal and wish to add a touch of personal style to your SFFPC, RGB RAM modules can be a fun choice. Prices for RGB and non-RGB RAM modules are typically similar, so this decision ultimately boils down to your personal preferences and whether you prefer the vibrant look or a more understated design for your system.

By thoughtfully considering these factors, you can ensure that your RAM selection aligns with the specific needs and objectives of your SFFPC build, ultimately contributing to a well-balanced and customized computing experience.
Power supply
Choosing the appropriate power supply unit (PSU) is a critical step in your Small Form Factor PC (SFFPC) build. Here are essential considerations to guide your PSU selection
Calculate Your System's Power Consumption
Once your system configuration is determined, you have the option to calculate the maximum power your system will consume. Fortunately, there are convenient tools available for this purpose, such as the Newegg Power Supply Calculator, where you simply input your build's components to obtain the power consumption estimate. For example, a setup featuring a Ryzen 7 7700X, a GeForce RTX 3070Ti graphics card, and 16GB of RAM may reach a consumption level of around 700 watts. In this scenario, opting for a 750W or 800W PSU would be advisable to ensure sufficient power for your system.
Safe bet : Corsair SF750
A highly regarded PSU for SFFPCs is the Corsair SF750. Priced at just a little over $150 and boasting an 80 Plus Gold certification, this PSU offers reliability, low noise operation, and minimal heat generation, making it an excellent fit for SFFPCs. The SF750 is known for its compact form factor, ideal for smaller cases, and delivers the power you need without compromising on efficiency or reliability.
By thoughtfully considering these factors and performing a power consumption calculation, you can ensure your PSU selection aligns with the specific requirements of your SFFPC build, providing the necessary power for your components while maintaining efficiency and reliability.
Cooling Systems
Effective cooling is a crucial consideration. Here is a brief overview of the most common cooling systems.
Air Cooling
Air cooling relies on large heatsinks and fans to dissipate heat from your components. While it's cost-effective and readily available, it can be relatively bulky and might generate more noise compared to other cooling options.
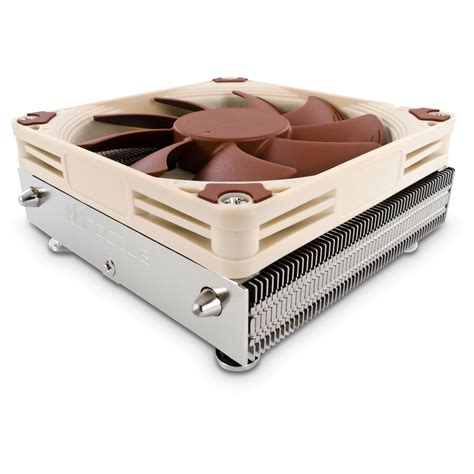

AIO (All-In-One) Liquid Cooling
AIO cooling systems combine elements of both air and liquid cooling. They consist of a fluid circuit with a radiator that features one, two, or even three fans. AIO coolers are known for their excellent efficiency, requiring minimal maintenance. Over the years, their reliability has significantly improved. Although they are pricier than air coolers, their cost-to-performance ratio is compelling. A 240mm AIO cooler, ideal for SFFPCs, typically costs around $100. If it fits in your case, it's a solid choice.
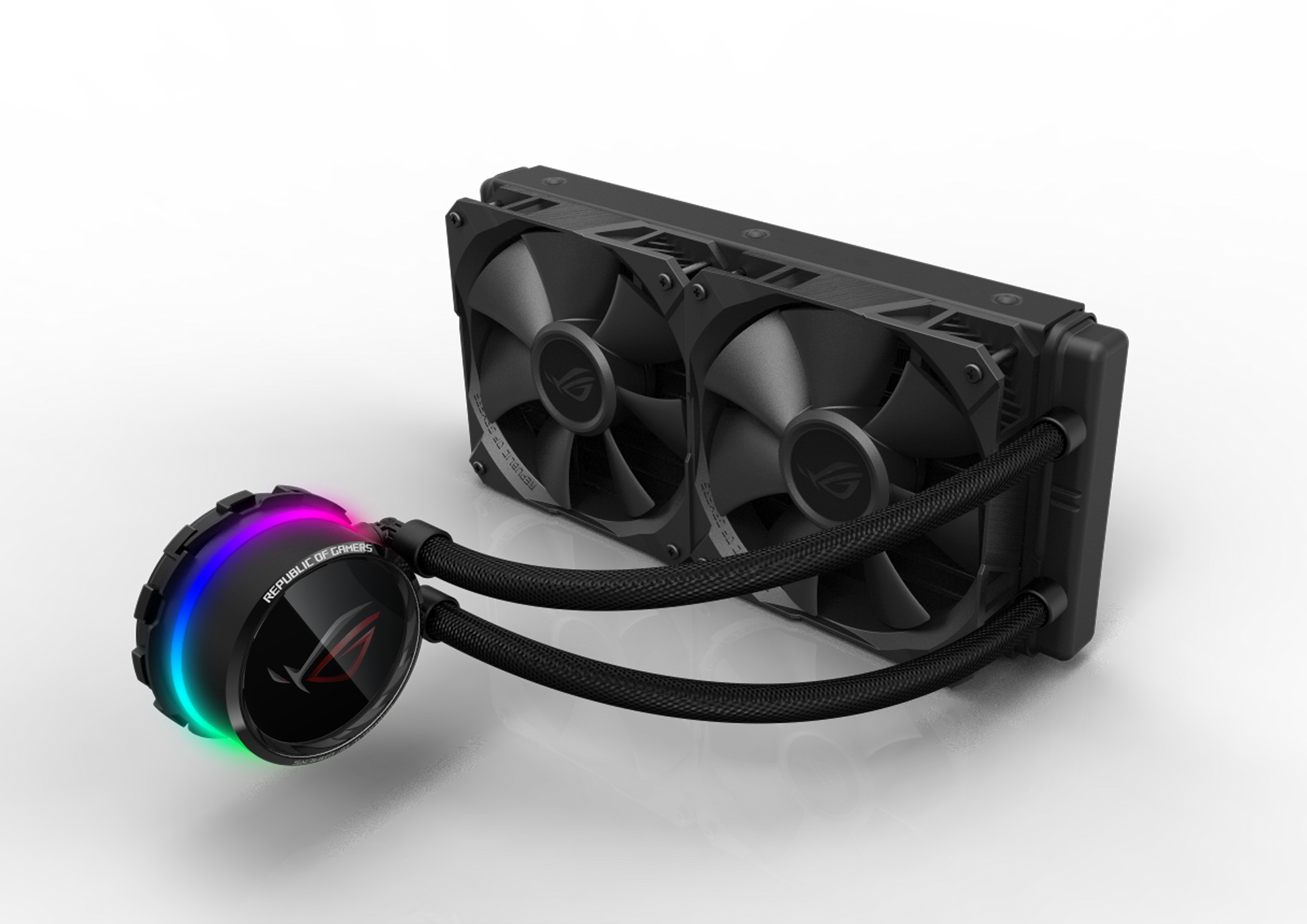

Custom Liquid Cooling Loop
For the DIY enthusiasts with deep pockets, custom liquid cooling loops offer an irresistible aesthetic. They allow for personalization, letting you choose the liquid color to match your preferences. However, these systems can be extremely expensive, with costs easily adding up for tubing, fittings, reservoirs, and pumps, often reaching around $800 or more. Furthermore, due to their complexity, custom liquid cooling systems are more susceptible to issues like leaks and malfunctions. Nevertheless, water cooling remains the most efficient cooling solution, capable of adapting to your graphics card, delivering exceptional silence and outstanding performance—when it's working as intended.
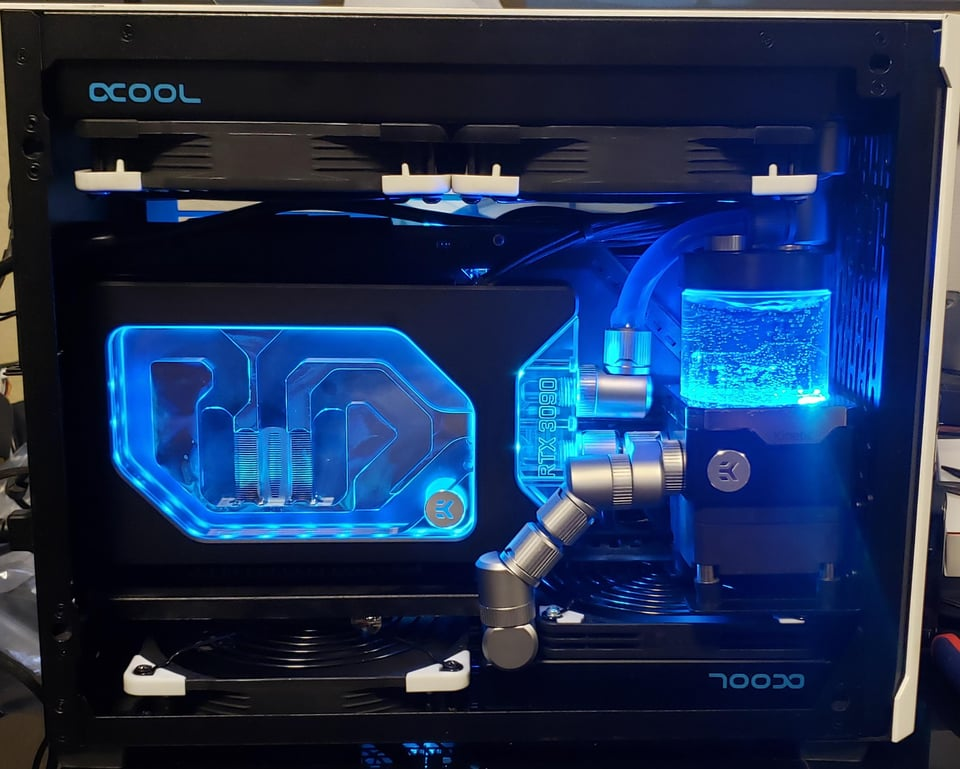

Each cooling system has its advantages and drawbacks, making it essential to consider your priorities and budget when selecting the right cooling solution for your SFFPC build.
Cable Management
Finally, let's address the issue of cables. Power supply units come with relatively long cables designed to accommodate a wide range of PC configurations. While this versatility is beneficial, it may not be the best fit for your specific SFFPC build. Consequently, you'll be left with a multitude of cables to manage neatly, adding another layer to the challenges of building an SFFPC.

Fortunately, some online stores offer custom-made cables tailored to specific cases or requirements. These cables can be customized in terms of color, and some even support RGB lighting, allowing you to further personalize your build. However, this level of customization comes at a price. Some custom cables can cost up to $50 each, and you'll likely need at least three or four to ensure your SFFPC looks both clean and organized.

Efficient cable management is a vital aspect of your SFFPC build, as it not only enhances the aesthetics of your system but also aids in optimizing airflow and cooling. So, while it may add an extra expense, it's an investment that can greatly improve the overall functionality and appearance of your compact powerhouse.
Conclusion
Picking the right components takes time and you should take it if you want to complete and enjoy the sffpc of your dreams.
In my next article, I'll address the selection of the case which should naturally come at the end of the selection process to be sure that everything fits in with ideal thermal conditions.